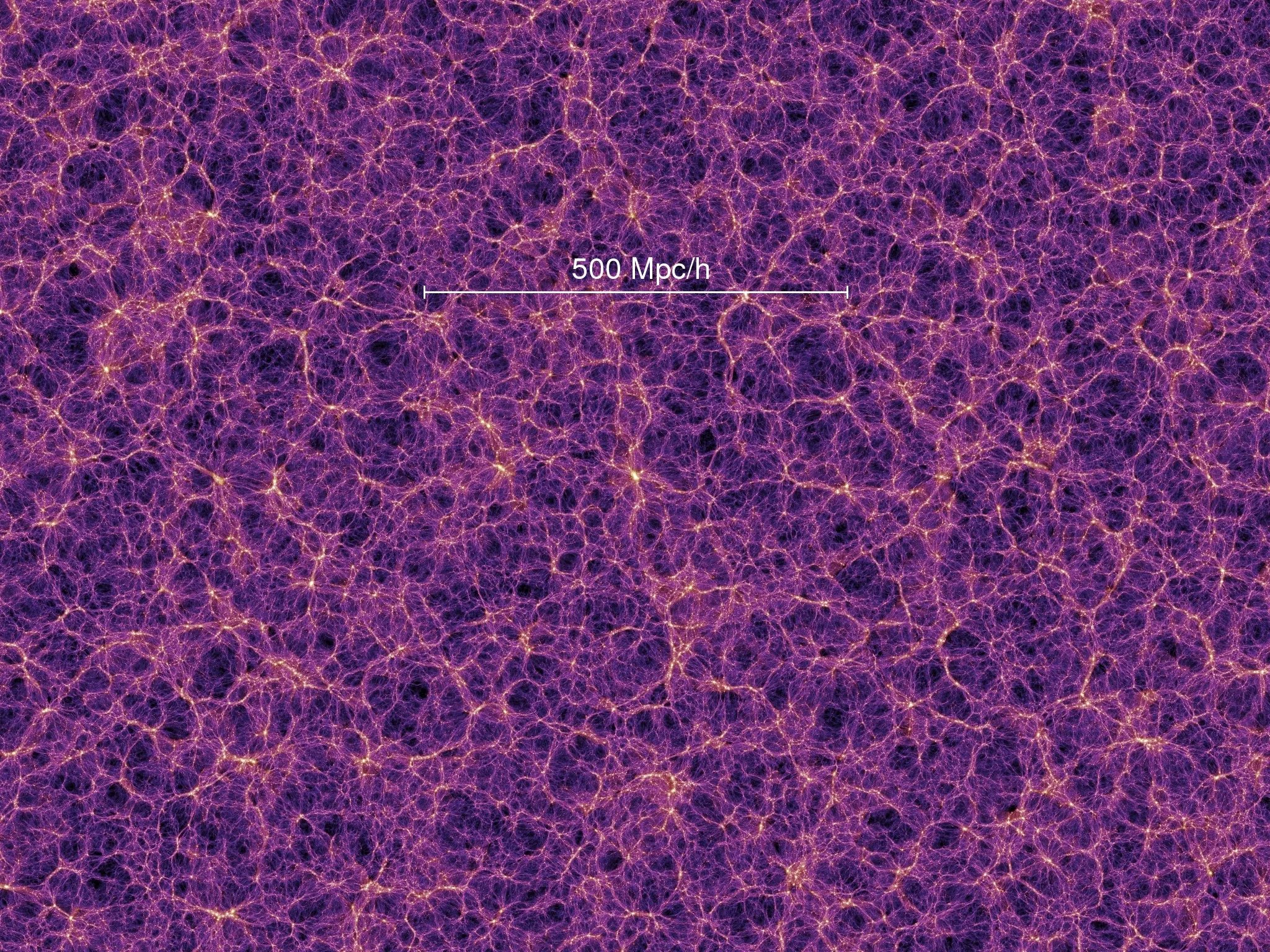
Our Universe
-

The Observable Universe
The observable universe is the part of space that can be seen by humans using technology. It's a ball-shaped region that includes all matter that can be observed from Earth or space-based telescopes and probes. The observable universe is about 93 billion light-years in diameter, and is centered on Earth.
-

The Entire Universe
The term "entire universe" refers to everything that exists, including all of space, time, matter, and energy. It also includes the physical laws that govern matter and energy, such as relativity, classical mechanics, and conservation laws. The word "entire" emphasizes that the term refers to the whole of something.
-

Multiverse
The multiverse is a hypothetical collection of universes that some scientists and cosmologists believe may exist beyond the observable universe. The multiverse is thought to contain everything that exists, including space, time, matter, energy, information, and the physical laws that govern them.
-

Space Time
1. A system of one temporal and three spatial coordinates by which any physical object or event can be located. called also space-time continuum.
2. The whole or a portion of physical reality determinable by a usually four-dimensional coordinate system.
-

Multiple Dimensions
Multidimensional means having many different aspects, elements, or factors. For example, you might describe a problem as multidimensional, such as a crime or international terrorism. You could also describe a relationship as multidimensional if the people involved are at different levels in terms of their energy, expectations, abilities, vision, and motivation.
-

Our Solar System
The collection of eight planets and their moons in orbit around the sun, together with smaller bodies in the form of asteroids, meteoroids, and comets. The planets of the solar system are (in order of distance from the sun) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.